Why Install Electric Vehicle Chargers?
In 2022, according to the World Economic Forum, one in seven cars purchased globally were fully electric with countries such as Norway leading the way, where 79% of all car purchases were electric vehicles. The increase in electric vehicle (EV) purchases means that more charging stations are necessary to keep up with this consumer demand. While traditional gas stations must have the space and capacity to store large amounts of fuel, EV charging stations only require a physical connection to an energy source and a vehicle charging plug. Since most modern buildings in the US are connected to an electricity grid, any business can serve as the “gas station” of the future.
Why Install Electric Vehicle Charging at Your Business?
We are seeing businesses from all industries and different geographic regions installing EV chargers at their facilities. There are a number of factors that are driving businesses to install these charging stations. These factors include employee engagement, company sustainability initiatives, and a means to drive more vehicular traffic to a business. Companies are beginning to offer electric vehicle charging in their parking lots as an incentive for interested employees as a perk of their employment. With the proper charger, EV charge times can coincide with working hours in a way that employee cars are fully charged by the end of the workday. Additionally, vehicle chargers at a commercial or industrial facility can help that business to reduce its Scope 3 emissions or Scope 1 emissions in the case of fleet vehicles. Finally, with the advent of mapping technology such as PlugShare, EV drivers can identify businesses with chargers. This technology can be used to incentivize EV owners to stop and make purchases while their vehicle is charging. The first step in the charger installation process is to determine the kind of charger to install.
Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Chargers
There are three types of electric vehicle chargers: Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Chargers (see Figure 1). Level 1 chargers typically come with an electric vehicle purchase and will plug into a traditional 120 V outlet for one’s home. These chargers can take 20+ hours to charge a vehicle to 100% and are typically used at locations where one can charge overnight. These are the least expensive chargers and do not require any infrastructure modifications or upgrades. These lengthy charge times will not work for most businesses. Level 2 chargers typically require between 5 and 6 hours to fully charge a car and require a 240V outlet, the same as a typical domestic washer or dryer would require. Level 2 chargers may require the installation of additional outlets or other infrastructure improvements. In these instances, it is important to consult a qualified electrician and the utility before the installation of these chargers. DC Fast chargers can achieve full charge in as little as 30 minutes. Tesla and ChargePoint are two major public charging companies that host DC Fast chargers that are accessible to the public. For businesses, the decision to choose between Level 2 and DC Fast chargers is dependent on the amount of time one expects a given vehicle to remain at a parking facility. Level 2 chargers are likely adequate for businesses that want to offer employees a way to charge their vehicles, while DC Fast chargers are a better option for businesses that intend to offer chargers for retail shoppers.
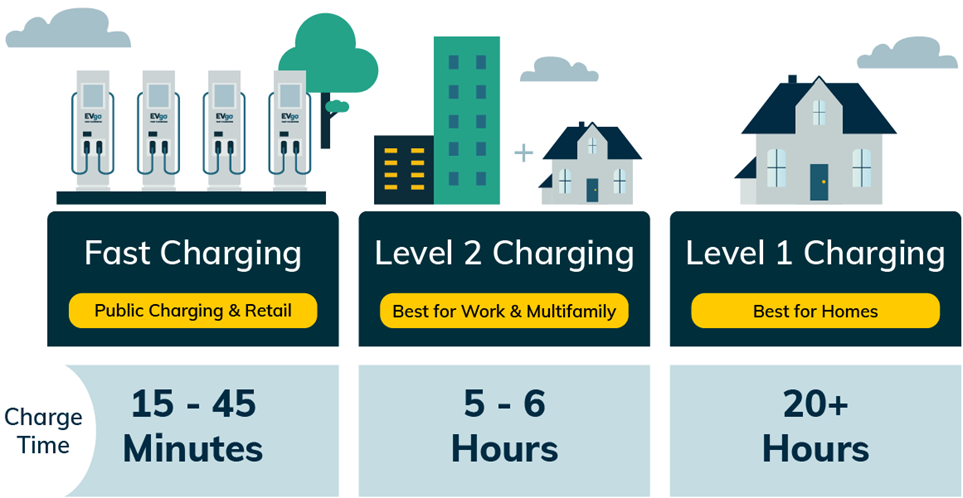
Figure 1: EVgo.com
Existing EV Incentives
Today, EV charging is still in its infancy and there are not enough charging stations available for full-scale commercial adoption. Federal incentives for EV chargers have been incorporated into the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) to incentivize businesses to increase the number of EV chargers available to the public. The specific provision in the IRA is called the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Formula Program (NEVI). NEVI places the responsibility on each state’s department of transportation to produce a plan that will deploy charging stations every 40 miles along major US highways. Outside of the federal incentives associated with NEVI, there are also local incentives in states such as New York, where 80% of the cost for DC Fast chargers can be covered through NYSERDA funding.
The EV revolution is here and charging stations are an obviously critical component to putting more EVs on the road. Higher employee engagement, compliance with sustainability initiatives, and more retail traffic are a few of the reasons to consider installing charging stations at your business. And while today, the number of EV charging stations remains small, federal, state, and local incentives seek to change that. These incentives and the opportunity to reduce your business’s carbon footprint are great reasons for your business to consider installing EV chargers. Reach out to your 5 Energy Advisor to find out how your business can take this next step in the energy transition.